
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Guideline/Fact Sheet
- Dyslipidemia Fact Sheet in South Korea, 2022
- Eun-Sun Jin, Jee-Seon Shim, Sung Eun Kim, Jae Hyun Bae, Shinae Kang, Jong Chul Won, Min-Jeong Shin, Heung Yong Jin, Jenny Moon, Hokyou Lee, Hyeon Chang Kim, In-Kyung Jeong, on Behalf of the Committee of Public Relation of the Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(5):632-642. Published online August 2, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0135

- 3,075 View
- 315 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
This study aimed to investigate the prevalence and status of dyslipidemia management among South Korean adults, as performed by the Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis under the name Dyslipidemia Fact Sheet 2022.
Methods
We analyzed the lipid profiles, age-standardized and crude prevalence, management status of hypercholesterolemia and dyslipidemia, and health behaviors among Korean adults aged ≥20 years, using the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data between 2007 and 2020.
Results
In South Korea, the crude prevalence of hypercholesterolemia (total cholesterol ≥240 mg/dL or use of a lipid-lowering drug) in 2020 was 24%, and the age-standardized prevalence of hypercholesterolemia more than doubled from 2007 to 2020. The crude treatment rate was 55.2%, and the control rate was 47.7%. The crude prevalence of dyslipidemia—more than one out of three conditions (low-density lipoprotein cholesterol ≥160 or the use of a lipid-lowering drug, triglycerides ≥200, or high-density lipoprotein cholesterol [HDL-C] [men and women] <40 mg/dL)—was 40.2% between 2016 and 2020. However, it increased to 48.2% when the definition of hypo-HDL-cholesterolemia in women changed from <40 to <50 mg/dL.
Conclusion
Although the prevalence of hypercholesterolemia and dyslipidemia has steadily increased in South Korea, the treatment rate remains low. Therefore, continuous efforts are needed to manage dyslipidemia through cooperation between the national healthcare system, patients, and healthcare providers. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Oxidative Balance Score and New-Onset Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Korean Adults without Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study-Health Examinees (KoGES-HEXA) Cohort
Mid-Eum Moon, Dong Hyuk Jung, Seok-Jae Heo, Byoungjin Park, Yong Jae Lee
Antioxidants.2024; 13(1): 107. CrossRef - Comparison of metabolic and neurological comorbidities in Asian patients with psoriasis and atopic dermatitis
Hee Joo Yang, Mi Young Lee, Jeong Hyeon Lee, Chang Jin Jung, Woo Jin Lee, Chong Hyun Won, Mi Woo Lee, Joon Min Jung, Sung Eun Chang
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Adding Apolipoprotein B Testing on the Prevalence of Dyslipidemia and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease in the Korean Adult Population
Rihwa Choi, Sang Gon Lee, Eun Hee Lee
Metabolites.2024; 14(3): 169. CrossRef - Exploring Utilization and Establishing Reference Intervals for the Apolipoprotein B Test in the Korean Population
Rihwa Choi, Sang Gon Lee, Eun Hee Lee
Diagnostics.2023; 13(20): 3194. CrossRef
- Oxidative Balance Score and New-Onset Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Korean Adults without Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study-Health Examinees (KoGES-HEXA) Cohort
- Lifestyle
- Ultra-Processed Food Consumption and Obesity in Korean Adults
- Jee-Seon Shim, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim, Hyeon Chang Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(4):547-558. Published online April 26, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0026
- 2,865 View
- 139 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
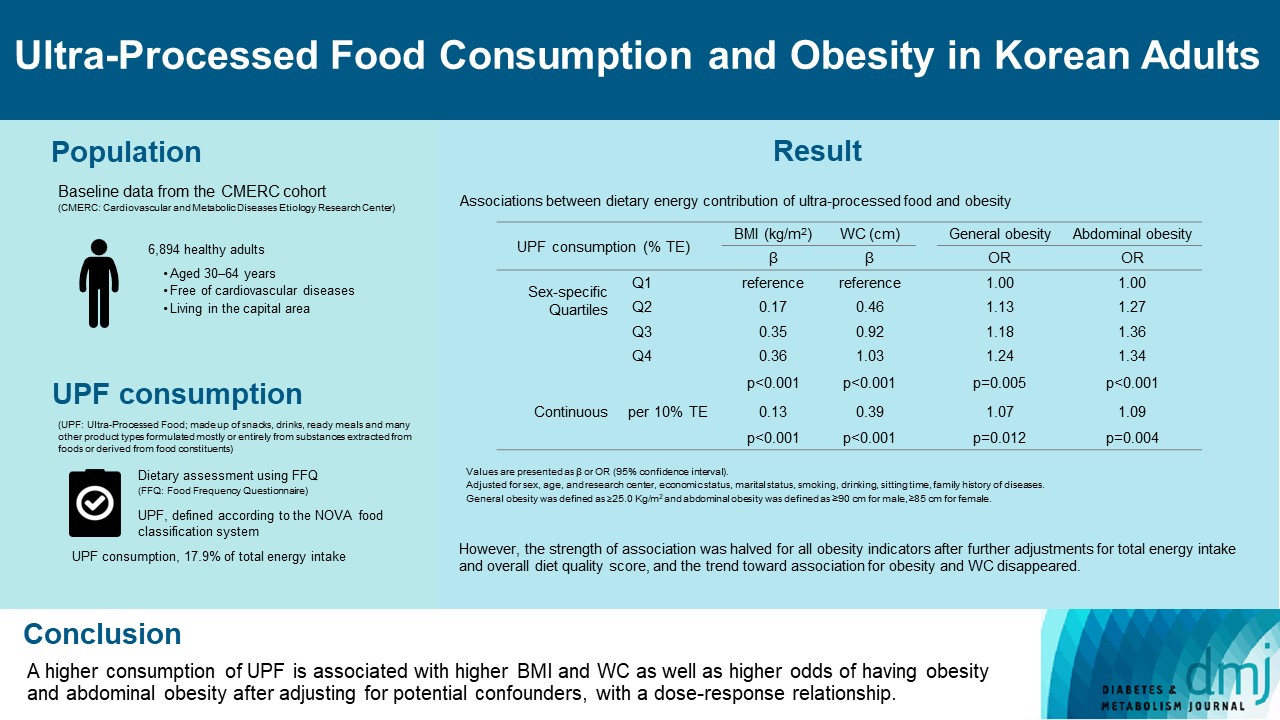
This study aimed to investigate the association between consumption of ultra-processed foods (UPF) and obesity in Korean adults.
Methods
We included the Cardiovascular and Metabolic Diseases Etiology Research Center cohort study baseline data of adults aged 30 to 64 years who completed a validated food frequency questionnaire. UPF was defined using the NOVA food classification. Multivariable linear and logistic regression analyses were performed to assess the association of dietary energy contribution of UPF with obesity indicators (body mass index [BMI], obesity, waist circumference [WC], and abdominal obesity).
Results
Consumption of UPF accounted for 17.9% of total energy intake and obesity and abdominal obesity prevalence was 35.4% and 30.2%, respectively. Compared with those in the lowest quartile of UPF consumption, adults in the highest quartile had greater BMI (β=0.36; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.15 to 0.56), WC (β=1.03; 95% CI, 0.46 to 1.60), higher odds of having obesity (odds ratio [OR], 1.24; 95% CI, 1.07 to 1.45), and abdominal obesity (OR, 1.34; 95% CI, 1.14 to 1.57), after adjusting for sociodemographic characteristics, health-related behaviors, and family history of diseases. Dose-response associations between UPF consumption and obesity indicators were consistently found (all P trend <0.01). However, the strength of association was halved for all obesity indicators after further adjustments for total energy intake and overall diet quality score, and the trend toward association for obesity and WC disappeared.
Conclusion
Our finding supports the evidence that consumption of UPF is positively associated with obesity among Korean adults. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Ultra-processed food consumption and increased risk of metabolic syndrome in Korean adults: A cross-sectional analysis of the KNHANES 2016–2020
Hansol Park, Youngmi Lee, Jinah Hwang, Yujin Lee
Nutrition.2024; 122: 112374. CrossRef - Diet quality partially mediates the association between ultraprocessed food consumption and adiposity indicators
Jee‐Seon Shim, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim, Hyeon Chang Kim
Obesity.2023; 31(9): 2430. CrossRef - Development of a Semi-Quantitative Food-Frequency Questionnaire for Korean Adults with Obesity
Jina Chung, Seoeun Ahn, Hyojee Joung, Sangah Shin
Nutrients.2023; 15(22): 4848. CrossRef
- Ultra-processed food consumption and increased risk of metabolic syndrome in Korean adults: A cross-sectional analysis of the KNHANES 2016–2020
- Complications
- Association of Snoring with Prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: The Cardiovascular and Metabolic Diseases Etiology Research Center Cohort
- So Mi Jemma Cho, Hokyou Lee, Jee-Seon Shim, Hyeon Chang Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(5):687-698. Published online April 16, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0128
- 5,249 View
- 108 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
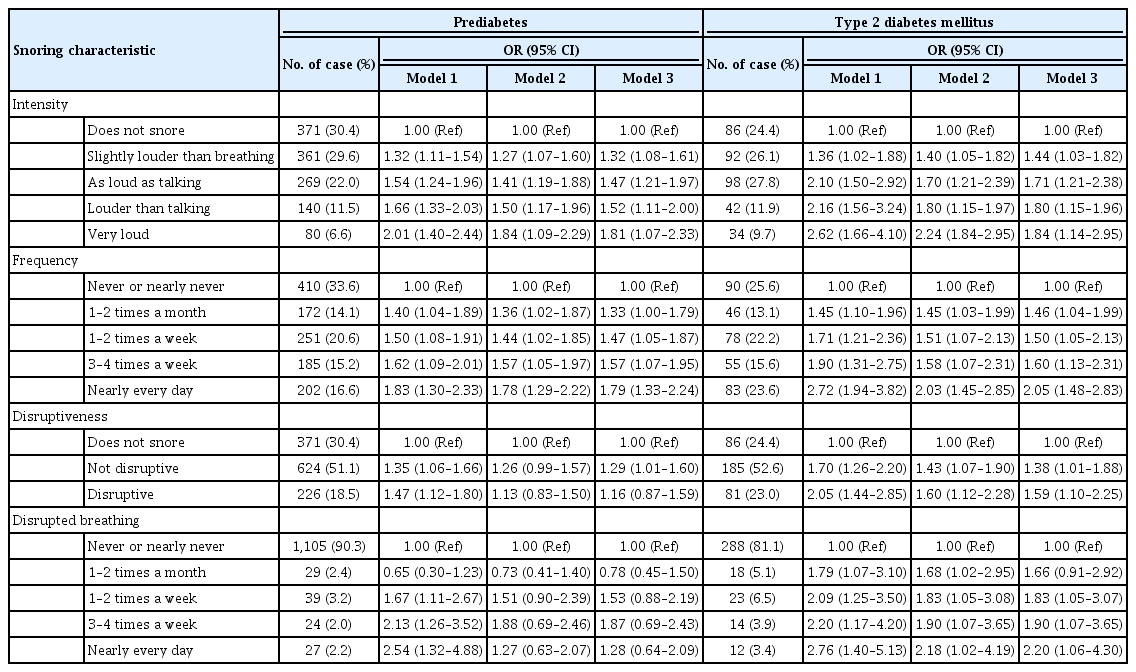
ePub Background Evidence suggests that habitual snoring is an independent risk factor for poor glycemic health. We examined the associations between snoring with prediabetes and diabetes in Korean population.
Methods Self-reported snoring characteristics were collected from 3,948 middle-aged adults without prior cardiovascular diseases. Multivariable linear regression assessed the association of snoring intensity, frequency, disruptiveness, and disrupted breathing with fasting glucose and glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) level. Then, multinomial regression evaluated how increasing snoring symptoms are associated with the risk for prediabetes and diabetes, adjusting for socioeconomic and behavioral risk factors of diabetes, obesity, hypertension, and other sleep variables.
Results Higher snoring intensity and frequency were positively associated with fasting glucose and HbA1c levels. Participants presenting the most severe snoring were at 1.84 times higher risk (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.09 to 2.29) for prediabetes and 2.24 times higher risk (95% CI, 1.84 to 2.95) for diabetes, compared to non-snorers. Such graded association was also observed amongst the most frequent snorers with higher risk for prediabetes (odds ratio [OR], 1.78; 95% CI, 1.29 to 2.22) and diabetes (OR, 2.03; 95% CI, 1.45 to 2.85). Disruptive snoring (OR, 1.60; 95% CI, 1.12 to 2.28) and near-daily disruptive breathing (OR, 2.18; 95% CI, 1.02 to 4.19) were associated with higher odds for diabetes. Such findings remained robust after additional adjustment for sleep duration, excessive daytime sleepiness, unwakefulness, and sleep-deprived driving.
Conclusion Snoring is associated with impaired glucose metabolism even in otherwise metabolically healthy adults. Habitual snorers may require lifestyle modifications and pharmacological treatment to improve glycemic profile.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Does seasonality affect snoring? A study based on international data from the past decade
Ping Wang, Cai Chen, Xingwei Wang, Ningling Zhang, Danyang Lv, Wei Li, Fulai Peng, Xiuli Wang
Sleep and Breathing.2023; 27(4): 1297. CrossRef - Association Between Snoring and Diabetes Among Pre- and Postmenopausal Women
Yun Yuan, Fan Zhang, Jingfu Qiu, Liling Chen, Meng Xiao, Wenge Tang, Qinwen Luo, Xianbin Ding, Xiaojun Tang
International Journal of General Medicine.2022; Volume 15: 2491. CrossRef - Elevated fasting insulin results in snoring: A view emerged from causal evaluation of glycemic traits and snoring
Minhan Yi, Quanming Fei, Kun Liu, Wangcheng Zhao, Ziliang Chen, Yuan Zhang
European Journal of Clinical Investigation.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Sleeping Duration, Napping and Snoring in Association with Diabetes Control among Patients with Diabetes in Qatar
Hiba Bawadi, Asma Al Sada, Noof Al Mansoori, Sharifa Al Mannai, Aya Hamdan, Zumin Shi, Abdelhamid Kerkadi
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(8): 4017. CrossRef - Changes in creatinine‐to‐cystatin C ratio over 4 years, risk of diabetes, and cardiometabolic control: The China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study
Shanhu Qiu, Xue Cai, Yang Yuan, Bo Xie, Zilin Sun, Tongzhi Wu
Journal of Diabetes.2021; 13(12): 1025. CrossRef - Association Between Self-Reported Snoring and Metabolic Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Jinsha Ma, Huifang Zhang, Hui Wang, Qian Gao, Heli Sun, Simin He, Lingxian Meng, Tong Wang
Frontiers in Neurology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Early Development of Bidirectional Associations between Sleep Disturbance and Diabetes
Yongin Cho
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(5): 668. CrossRef
- Does seasonality affect snoring? A study based on international data from the past decade
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Sex-, Age-, and Metabolic Disorder-Dependent Distributions of Selected Inflammatory Biomarkers among Community-Dwelling Adults
- So Mi Jemma Cho, Hokyou Lee, Jee-Seon Shim, Hyeon Chang Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(5):711-725. Published online April 16, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0119
- 5,925 View
- 83 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
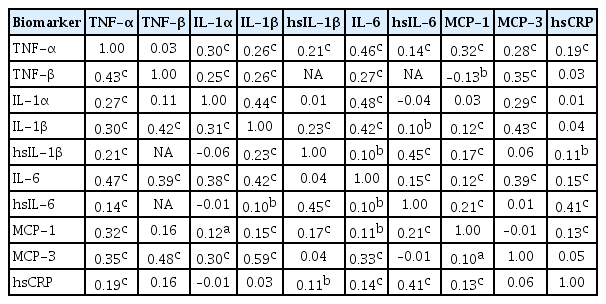
ePub Background Inflammatory cytokines are increasingly utilized to detect high-risk individuals for cardiometabolic diseases. However, with large population and assay methodological heterogeneity, no clear reference currently exists.
Methods Among participants of the Cardiovascular and Metabolic Diseases Etiology Research Center cohort, of community-dwelling adults aged 30 to 64 without overt cardiovascular diseases, we presented distributions of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α and -β, interleukin (IL)-1α, -1β, and 6, monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP)-1 and -3 and high sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) with and without non-detectable (ND) measurements using multiplex enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Then, we compared each markers by sex, age, and prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and dyslipidemia, using the Wilcoxon Rank-Sum Test.
Results In general, there were inconsistencies in direction and magnitude of differences in distributions by sex, age, and prevalence of cardiometabolic disorders. Overall, the median and the 99th percentiles were higher in men than in women. Older participants had higher TNF-α, high sensitivity IL-6 (hsIL-6), MCP-1, hsCRP, TNF-β, and MCP-3 median, after excluding the NDs. Participants with type 2 diabetes mellitus had higher median for all assayed biomarkers, except for TNF-β, IL-1α, and MCP-3, in which the medians for both groups were 0.00 due to predominant NDs. Compared to normotensive group, participants with hypertension had higher TNF-α, hsIL-6, MCP-1, and hsCRP median. When stratifying by dyslipidemia prevalence, the comparison varied significantly depending on the treatment of NDs.
Conclusion Our findings provide sex-, age-, and disease-specific reference values to improve risk prediction and diagnostic performance for inflammatory diseases in both population- and clinic-based settings.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Characterizing CD8+ TEMRA Cells in CP/CPPS Patients: Insights from Targeted Single-Cell Transcriptomic and Functional Investigations
Fei Zhang, Qintao Ge, Jialin Meng, Jia Chen, Chaozhao Liang, Meng Zhang
ImmunoTargets and Therapy.2024; Volume 13: 111. CrossRef - Association between physical activity and inflammatory markers in community-dwelling, middle-aged adults
So Mi Jemma Cho, Hokyou Lee, Jee-Seon Shim, Justin Y. Jeon, Hyeon Chang Kim
Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism.2021; 46(7): 828. CrossRef - The monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio: Sex-specific differences in the tuberculosis disease spectrum, diagnostic indices and defining normal ranges
Thomas S. Buttle, Claire Y. Hummerstone, Thippeswamy Billahalli, Richard J. B. Ward, Korina E. Barnes, Natalie J. Marshall, Viktoria C. Spong, Graham H. Bothamley, Selvakumar Subbian
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(8): e0247745. CrossRef
- Characterizing CD8+ TEMRA Cells in CP/CPPS Patients: Insights from Targeted Single-Cell Transcriptomic and Functional Investigations
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Association between the Thigh Muscle and Insulin Resistance According to Body Mass Index in Middle-Aged Korean Adults
- Ji Eun Heo, Jee-Seon Shim, Hokyou Lee, Hyeon Chang Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(3):446-457. Published online April 16, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0110
- 6,746 View
- 89 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background We examined the associations between thigh muscle area (TMA) and insulin resistance (IR) according to body mass index (BMI) in middle-aged Korean general population.
Methods TMA was measured using quantitative computed tomography and corrected by body weight (TMA/Wt) in 1,263 men, 788 premenopausal women, and 1,476 postmenopausal women all aged 30 to 64 years. The tertiles of TMA/Wt were calculated separately for men and for premenopausal and postmenopausal women. Homeostatic model assessment for insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) was performed using fasting blood glucose and insulin levels, and increased IR was defined according to sex-specific, top quartiles of HOMA-IR. Associations between the TMA/Wt tertiles and increased IR according to the BMI categories (<25 and ≥25 kg/m2) were assessed using multivariable logistic regression analysis.
Results In men with higher BMIs, but not in those with lower BMIs, the presence of an increased IR had significantly higher odds ratios in the lower TMA/Wt tertiles, even after adjustment for visceral fat area. However, in premenopausal and postmenopausal women, there was no significant inverse association between TMA/Wt tertiles and increased IR, regardless of BMI category.
Conclusion Our findings suggest that the thigh muscle is inversely associated with IR in men, particularly in those with higher BMIs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Risk of sleep apnea associated with higher blood pressure among Chinese and Korean Americans
Brittany N. Morey, Yuxi Shi, Soomin Ryu, Susan Redline, Ichiro Kawachi, Hye Won Park, Sunmin Lee
Ethnicity & Health.2024; 29(3): 295. CrossRef - Sex-specific equations to estimate body composition: Derivation and validation of diagnostic prediction models using UK Biobank
Yueqi Lu, Ying Shan, Liang Dai, Xiaosen Jiang, Congying Song, Bangwei Chen, Jingwen Zhang, Jing Li, Yue Zhang, Junjie Xu, Tao Li, Zuying Xiong, Yong Bai, Xiaoyan Huang
Clinical Nutrition.2023; 42(4): 511. CrossRef - Gender Differences in Relation to Body Composition, Insulin Resistance, and Islet Beta Cell Function in Newly Diagnosed Diabetic or Pre-Diabetic Patients
Minglei Ma, Tao Jiang, Zhen Wen, Dongxue Zhang, Lei Xiu
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2023; Volume 16: 723. CrossRef - Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease with Sarcopenia and Carotid Plaque Progression Risk in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Yongin Cho, Hye-Sun Park, Byung Wook Huh, Yong-ho Lee, Seong Ha Seo, Da Hea Seo, Seong Hee Ahn, Seongbin Hong, So Hun Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(2): 232. CrossRef - Prospective External Validation of an Algorithm Predicting Hourly
Basal Insulin Infusion Rates from Characteristics of Patients with Type 1
Diabetes Treated with Insulin Pumps
Jana S. Schmelzer, Melanie Kahle-Stephan, Juris J. Meier, Michael A. Nauck
Experimental and Clinical Endocrinology & Diabetes.2023; 131(10): 539. CrossRef - Establishing reference values for percentage of appendicular skeletal muscle mass and their association with metabolic syndrome in Korean adolescents
Da Hye Lee, Sung-Chan Kang, Seung-Sik Hwang, Yun Jeong Lee, Hwa Young Kim, Seong Yong Lee, Choong Ho Shin, Jaehyun Kim
Annals of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 28(4): 237. CrossRef - Evaluating Triglyceride and Glucose Index as a Simple and Easy-to-Calculate Marker for All-Cause and Cardiovascular Mortality
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, You-Cheol Hwang, Hong-Yup Ahn, Cheol-Young Park
Journal of General Internal Medicine.2022; 37(16): 4153. CrossRef - Association between Lower-to-Upper Ratio of Appendicular Skeletal Muscle and Metabolic Syndrome
Hyun Eui Moon, Tae Sic Lee, Tae-Ha Chung
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(21): 6309. CrossRef
- Risk of sleep apnea associated with higher blood pressure among Chinese and Korean Americans
- Epidemiology
- Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Concentration Is Independently Inversely Associated with Insulin Resistance in the Healthy, Non-Obese Korean Population
- So Young Ock, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Bu Kyung Kim, Hyeon Chang Kim, Jee-Seon Shim, Myung Ha Lee, Young Me Yoon, Dae Jung Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2016;40(5):367-375. Published online July 26, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2016.40.5.367
- 3,735 View
- 31 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background We evaluated the associations between 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) concentrations in serum and insulin resistance in the healthy Korean population.
Methods We conducted this cross-sectional analysis in 1,807 healthy Korean people (628 men and 1,179 women) aged 30 to 64 years in the Cardiovascular and Metabolic Disease Etiologic Research Center study. All participants were assessed for 25(OH)D, fasting glucose, and insulin levels, and completed a health examination and lifestyle questionnaire according to standard procedures. Insulin resistance was defined as the homeostasis model assessment insulin resistance higher than the 75 percentile.
Results Compared to those in the highest tertile (≥14.3 ng/mL), the odds ratio (OR) for insulin resistance was 1.37 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.01 to 1.86) for the 1st tertile (<9.7 ng/mL) and 1.19 (95% CI, 0.08 to 1.62) for the 2nd tertile (9.7 to 14.3 ng/mL) after adjusting for age, gender, waist circumference, alcohol consumption, smoking status, physical exercise, season, and cohort. After stratification of the subjects by adiposity, these associations remained only in non-obese subjects (lowest tertile vs. highest tertile, multivariable OR, 1.64; 95% CI, 1.05 to 2.56).
Conclusion Serum 25(OH)D has an independent inverse association with insulin resistance in the healthy, non-obese Korean population, even among people with vitamin D insufficiency.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Vitamin D and Cardiovascular Diseases: An Update
Farrookh Haider, Hashsaam Ghafoor, Omar F Hassan, Khalid Farooqui, Ali O. Mohamed Bel Khair, Faryal Shoaib
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Vitamin D as predictor Marker of kidney disease in males with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Abeer J. Hassan, Sarmad Ajeel Hazzaa, Dunya Najim Alden Ahmed
Bionatura.2022; 7(2): 1. CrossRef - Vitamin D Effect on Ultrasonography and Laboratory Indices and Biochemical Indicators in the Blood: an Interventional Study on 12 to 18-Year-Old Children with Fatty Liver
Kokab Namakin, Mahya Hosseini, Mahmoud Zardast, Mahyar Mohammadifard
Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology & Nutrition.2021; 24(2): 187. CrossRef - The Association between Vitamin D and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Assessed by Controlled Attenuation Parameter
Nam Ju Heo, Hyo Eun Park, Ji Won Yoon, Min-Sun Kwak, Jong In Yang, Su Jin Chung, Jeong Yoon Yim, Goh Eun Chung
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 10(12): 2611. CrossRef - Association between serum 25-hydroxy vitamin D level and metabolic associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD)—a population-based study
Bo Wan, Yuan Gao, Yushan Zheng, Ruanqin Chen
Endocrine Journal.2021; 68(6): 631. CrossRef - Clinical factors correlated with vitamin D deficiency in patients with obesity scheduled for bariatric surgery: A single center experience
Vincenzo Pilone, Salvatore Tramontano, Carmen Cutolo, Federica Marchese, Antonio Maria Pagano, Federica Di Spirito, Luigi Schiavo
International Journal for Vitamin and Nutrition Research.2020; 90(3-4): 346. CrossRef - Cohort Profile: The Cardiovascular and Metabolic Diseases Etiology Research Center Cohort in Korea
Jee-Seon Shim, Bo Mi Song, Jung Hyun Lee, Seung Won Lee, Ji Hye Park, Dong Phil Choi, Myung Ha Lee, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim, Sungha Park, Won-Woo Lee, Yoosik Youm, Eui-Cheol Shin, Hyeon Chang Kim
Yonsei Medical Journal.2019; 60(8): 804. CrossRef - Cardiovascular and Metabolic Diseases Etiology Research Center (CMERC) cohort: study protocol and results of the first 3 years of enrollment
Jee-Seon Shim, Bo Mi Song, Jung Hyun Lee, Seung Won Lee, Ji Hye Park, Dong Phil Choi, Myung Ha Lee, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim, Sungha Park, Won-Woo Lee, Hyeon Chang Kim
Epidemiology and Health.2017; 39: e2017016. CrossRef - Vitamin D and coronary atherosclerosis
Dae Jung Kim
Osteoporosis and Sarcopenia.2017; 3(4): 201. CrossRef
- Vitamin D and Cardiovascular Diseases: An Update

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





